Kligler Iron Agar
Used to differentiate Enterobacteriaceae members based on their ability to ferment dextrose and lactose and to liberate sulfides.
- Description
- Composition
- Quality Control
- Microbial Test Results
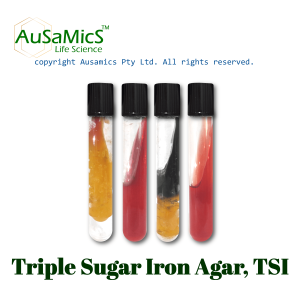
Kligler Iron Agar (KIA), a differential medium, is used to distinguish between Enterobacteriaceae strains based on their ability to ferment glucose and lactose as well as produce hydrogen sulfide. Peptones, yeast extract, glucose, lactose, ferric ammonium citrate, sodium thiosulfate, and phenol red are all present in the medium. Whereas non-lactose fermenters first ferment glucose, producing an acid slant and an alkaline butt, lactose fermenters produce acid throughout the tube. The generation of hydrogen sulfide is indicated by a black precipitate. Shigella and Salmonella are among the enteric pathogens that are thought to be identified using KIA.
Storage
Keep the container at 15-30 °C and prepared medium at 2-8 °C.
| Composition | gr/L |
| Peptone from Casein | 15 |
| Peptone from Meat | 5 |
| Meat Extract | 3 |
| Yeast Extract | 3 |
| Sodium Chloride | 5 |
| Lactose | 10 |
| Dextrose | 1 |
| Phenol Red | 0.024 |
| Sodium Thiosulfate | 0.5 |
| Ammonium Iron (III) Citrate | 0.5 |
| Agar | 12 |
| Final pH at 25°C | 7.4 ± 0.2 |
| Dehydrated Appearance | Fine, homogeneous, free of extraneous material |
| Prepared Appearance | Medium to dark, orange to red, with or without a tint of brown, clear to slightly hazy. |
| Reaction of 5.5% Solution at 25°C | pH 7.4 ± 0.2 |
| Incubate at 35±2 °C for 24 hours. | ||||
| Organism (ATCC) | Recovery | Slant | Butt | H2S |
| Salmonella enterica (14028) | Good | Alkaline | Acid w/o gas | + |
| Escherichia coli (25922) | Good | Acid | Acid w/ gas | – |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa (27853) | Good | Alkaline | Alkaline w/o gas | – |