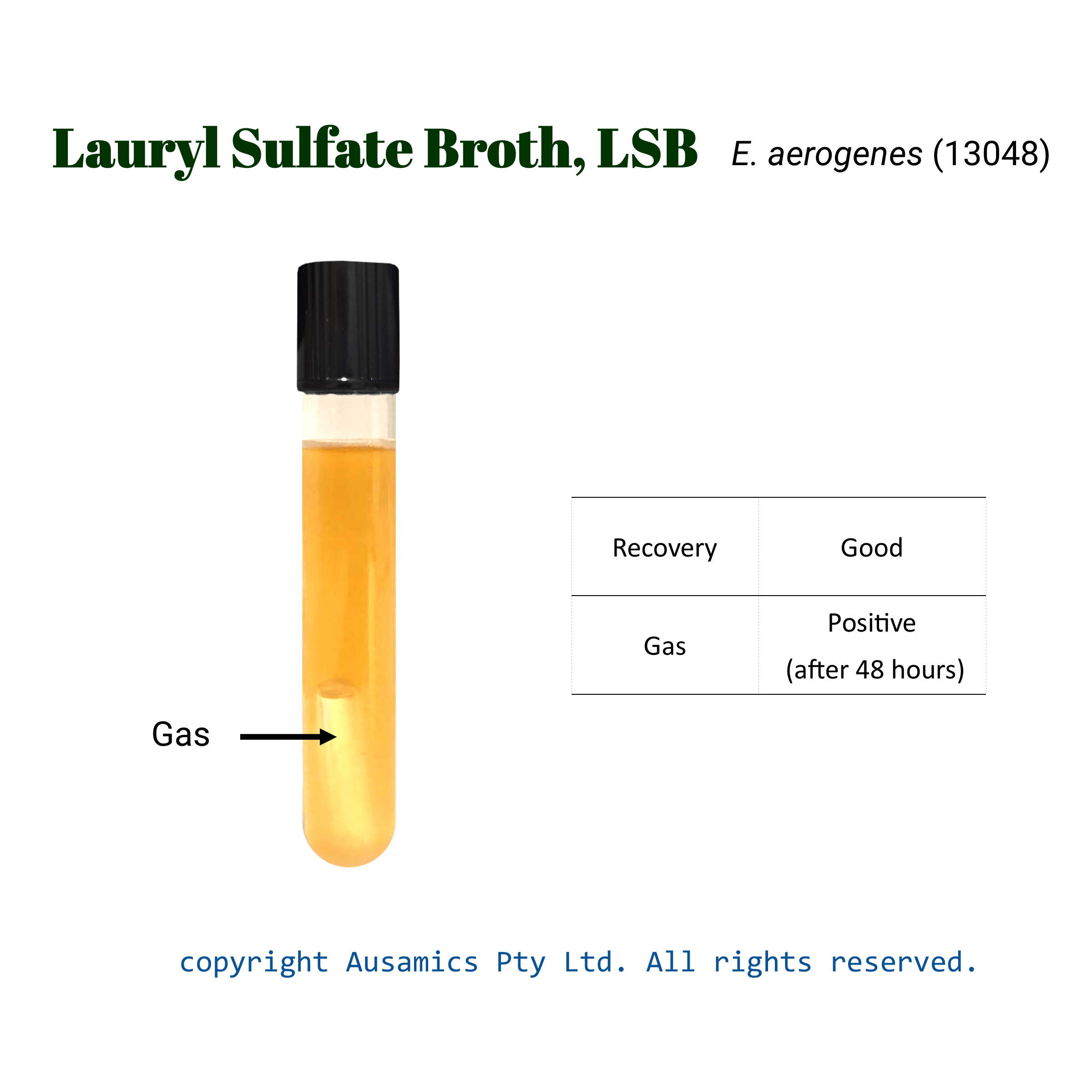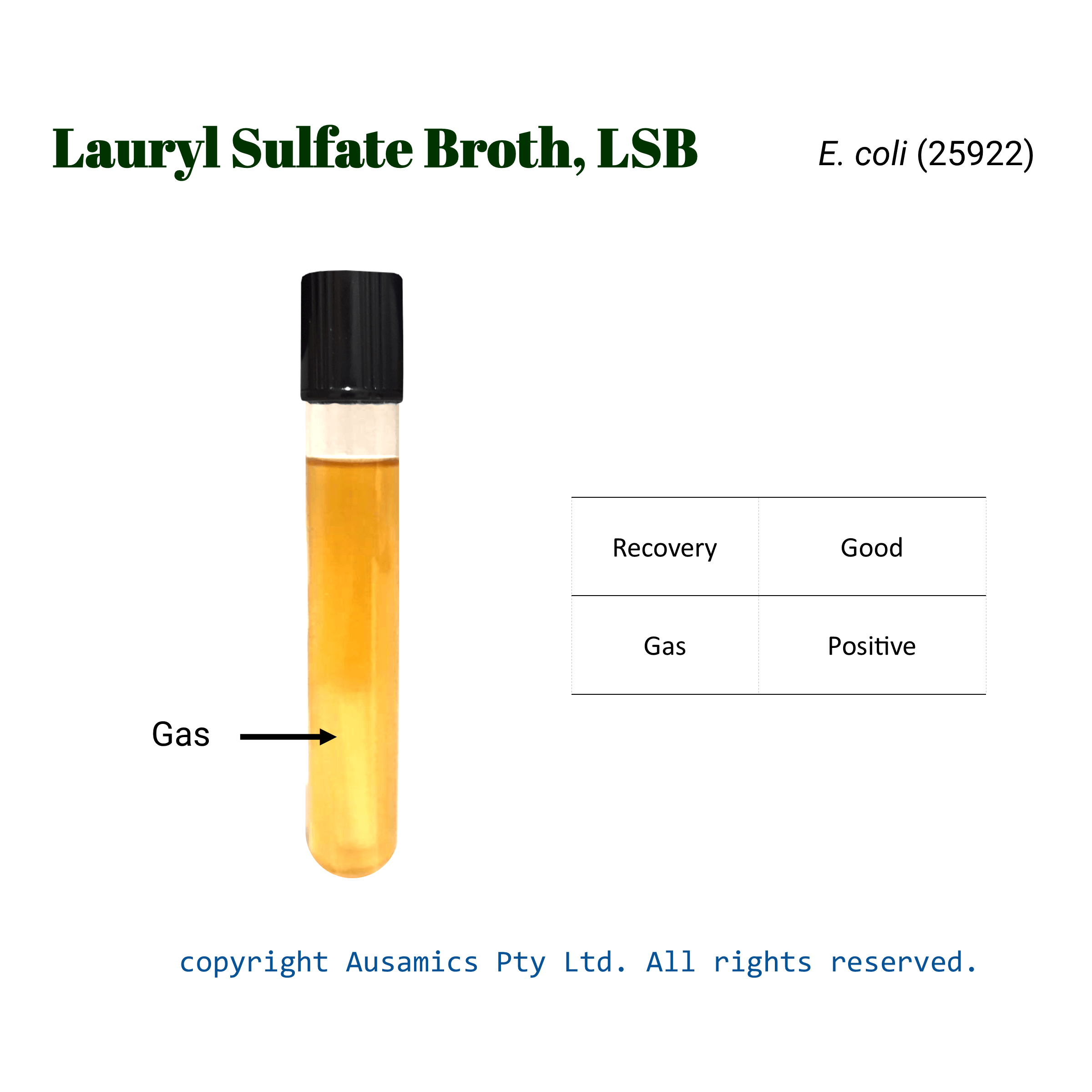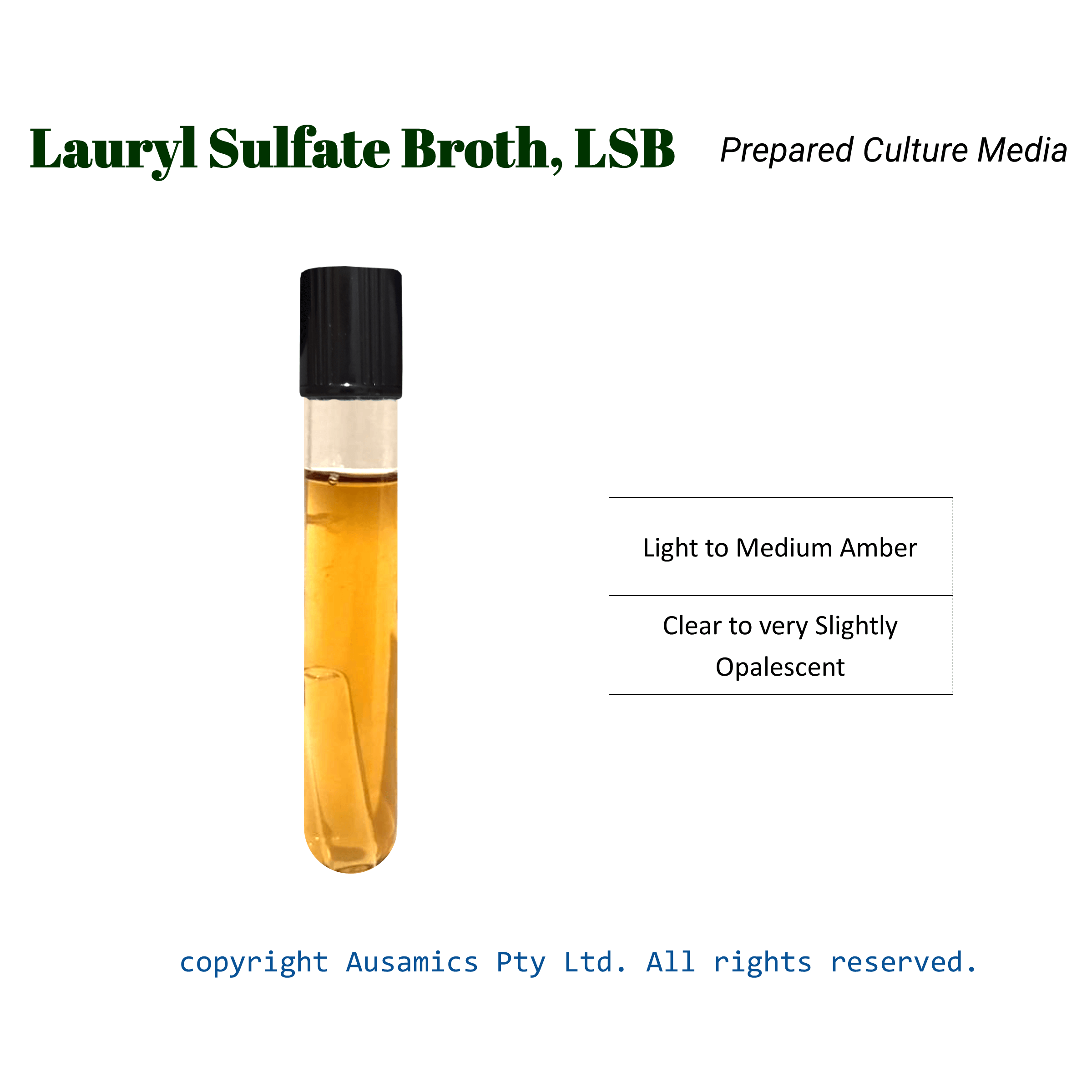Lauryl Sulfate Broth, LSB
Used for the detection of coliform organisms in water and wastewater, according to the formula of the APHA.
- Description
- Composition
- Quality Control
- Microbial Test Results
Lauryl Sulfate Broth (LSB), also called Lauryl Tryptose Broth (LTB), is a selective enrichment medium. It is used for the enumeration and presumed detection of coliform bacteria. Coliforms are facultative anaerobic, gram-negative microbes that digest lactose to create gas and acid. To supply vital nutrients, LTB includes tryptose, while sodium lauryl sulfate functions as a selective agent to prevent the growth of non-coliform organisms. Durham tubes show that the medium’s buffered nature promotes coliforms’ quick generation of gas. LSB is used in microbiological analyses of food, dairy, and water.
Storage
Keep the container at 15-30 °C and prepared medium at 2-8 °C.
| Composition | gr/L |
| Tryptose | 20 |
| Lactose | 5 |
| Dipotassium Phosphate | 2.75 |
| Monopotassium Phosphate | 2.75 |
| Sodium Chloride | 5 |
| Sodium Lauryl Sulfate | 0.1 |
| Final pH at 25°C | 6.8 ± 0.2 |
| Dehydrated Appearance | Light beige, free-flowing, homogeneous. |
| Prepared Appearance | Light to medium amber, clear to very slightly opalescent. |
| Reaction of 3.56% Solution at 25°C | pH 6.8 ± 0.2 |
| Incubate at 35±2 °C for 24 hours. | ||
| Organism (ATCC) | Recovery | Gas |
| Enterobacter aerogenes (13048) | Good | + |
| Escherichia coli (25922) | Good | + |
| Staphylococcus aureus (25923) | Marked to complete inhibition | – |