Sulfite Polymyxin Sulfadiazine Agar, SPS Agar
Used for isolation and enumeration of Clostridium perfringens and Clostridium botulinum in all types of foodstuffs.
- Description
- Composition
- Quality Control
- Microbial Test Results
SPS (Sulfite Polymyxin Sulfadiazine) Agar is a selective culture which is used to isolate and count Clostridium perfringens from a variety of food sources. To improve selectivity, sulfadiazine and polymyxin B sulfate are added to a base that is comparable to Wilson and Blair Agar.
Important components include ferric citrate and sodium sulfite as indicators of sulfide production, pancreatic digest of casein and yeast extract to supply vital nutrients, and polymyxin B and sulfadiazine as antibacterial agents to prevent competing microbiota.
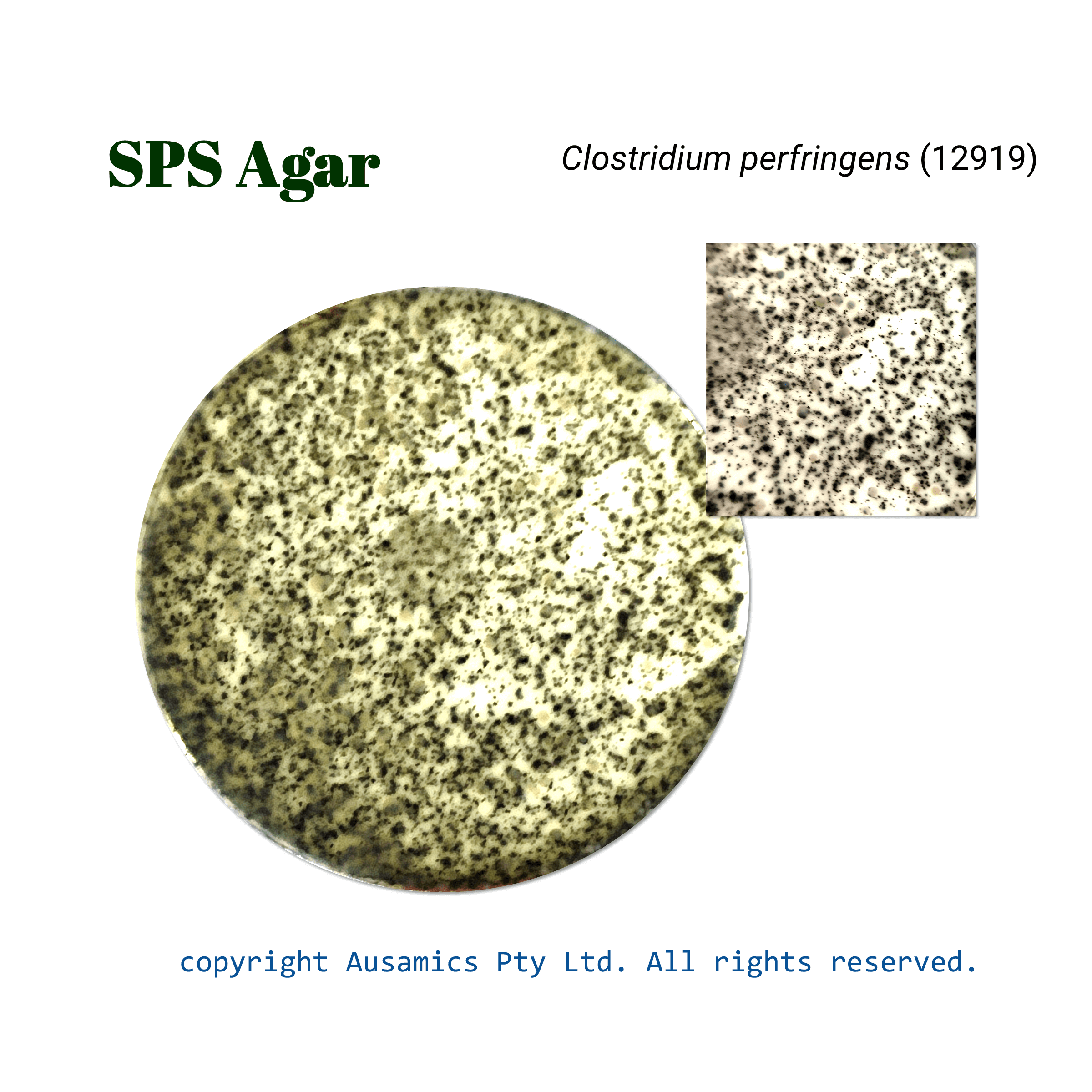
Black iron sulfide precipitates are formed when Clostridium perfringens converts sulfite to sulfide, which helps with colony differentiation. Although SPS Agar shows a moderate level of selectivity, more biochemical tests must be performed in order to definitively identify the species.
Storage
Keep the container at 15-30 °C and prepared medium at 2-8 °C.
| Composition | gr/L |
| Pancreatic digest of Casein | 15 |
| Yeast Extract | 10 |
| Ferric Citrate | 0.5 |
| Sodium Sulfite | 0.5 |
| Sulfadiazine | 0.12 |
| Polymyxin Sulfate | 0.01 |
| Agar | 13.9 |
| Final pH at 25°C | 7.0 ± 0.2 |
| Dehydrated Appearance | Beige, free-flowing, homogeneous. |
| Prepared Appearance | Light to medium amber, slightly opalescent. |
| Reaction of 4.0% Solution at 25°C | pH 7.0 ± 0.2 |
| Inoculate using pour plate technique and incubate at 35 ± 2 °C for 24 to 48 hours anaerobically. | ||
| Organism (ATCC) | Recovery | Colony color |
| Clostridium perfringens (12919) | Good | Black |
| Clostridium sporogenes (11437) | None to fair | Black |
| Escherichia coli (25922) | Marked to complete inhibition | – |
| Salmonella enterica (14028) | Marked to complete inhibition | – |
| Staphylococcus aureus (25923) | Fair to good | White |