Yeast Glucose Chloramphenicol Agar, YGC
Used for isolating and enumerating yeasts and molds in milk and dairy products.
- Description
- Composition
- Quality Control
- Microbial Test Results
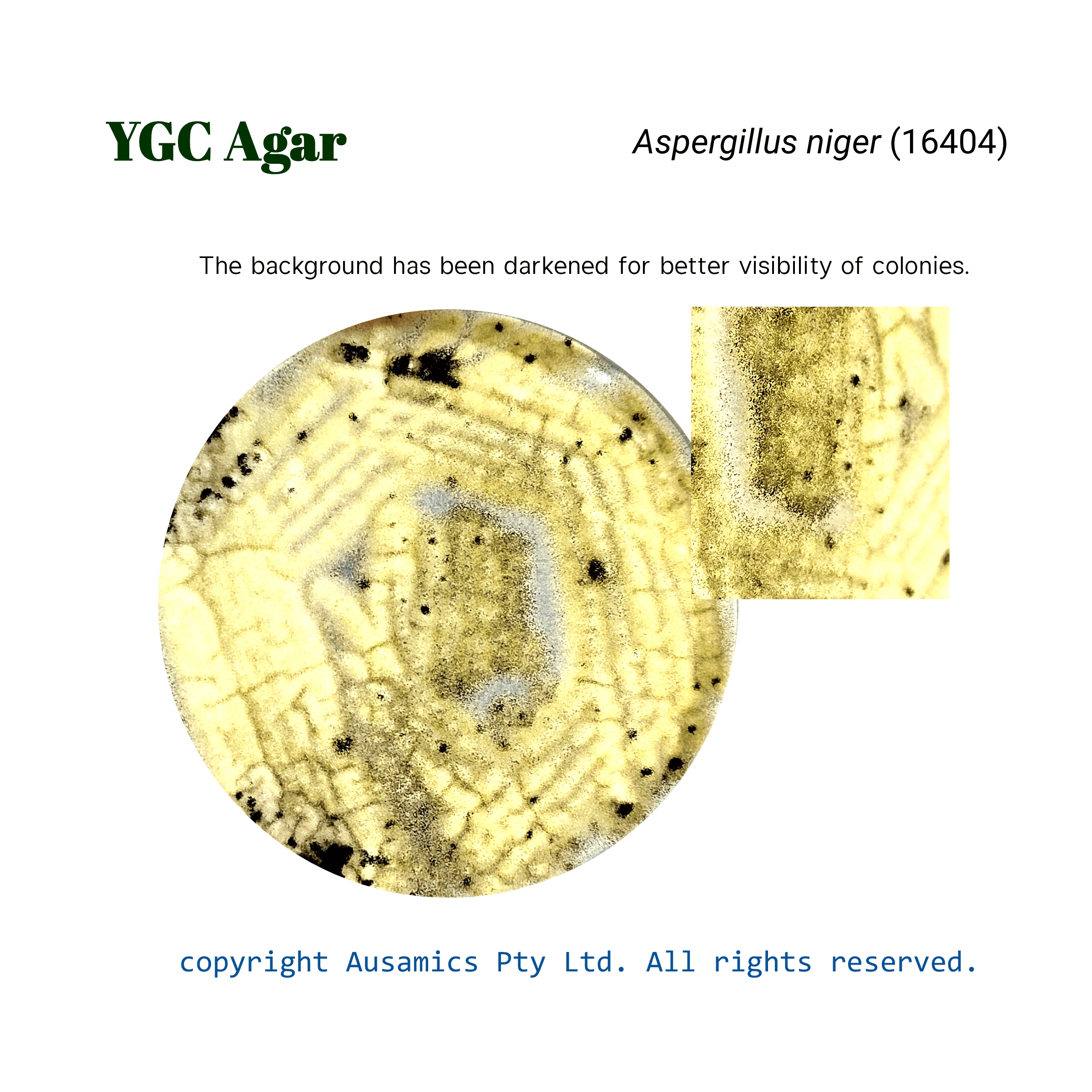
A selective culture medium called Yeast Glucose Chloramphenicol (YGC) Agar is used to count and isolate yeasts and molds. An antibiotic called chloramphenicol is added to the medium to specifically suppress bacterial growth and improve fungal colony recovery.
While glucose provides a carbon source for fungal metabolism, yeast extract supplies vital nutrients. A large variety of fungal species are supported in their growth by the combination of these elements. When reliable fungal counts are needed, YGC agar is frequently used in the microbiological analysis of food, dairy products, and other materials.
Storage
Keep the container at 15-30 °C and prepared medium at 2-8 °C.
| Composition | gr/L |
| Yeast extract | 5 |
| D (+) glucose | 20 |
| Chloramphenicol | 0.1 |
| Agar | 14.9 |
| Final pH at 25°C | 6.6 ± 0.2 |
| Dehydrated Appearance | Beige, free-flowing, homogeneous. |
| Prepared Appearance | Light amber, slightly opalescent. |
| Reaction of 4.0% Solution at 25°C | pH 6.6 ± 0.2 |
| Incubate at 25 ± 2 °C for up to 4 days. | |
| Organism (ATCC) | Recovery |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae (9763) | Good |
| Candida albicans (10231) | Good |
| Escherichia coli (25922) | Inhibition |
| Staphylococcus aureus (25923) | Inhibition |